Example Models
Several example models are provided in the install package.
Where to find
<install path>\examples\simulink
<install path> is usually: C:\openecu\platform\<version>
Opening from MATLAB
If OpenECU is correctly installed, type the following in the MATLAB console:
oe_examples
A model containing links to all the example models will open.
Models
Step1 completed
This model is an example of how to use the block set to make a simple OpenECU application. It is identical to the model you will create when doing the Step1 exercise described in the user guide.
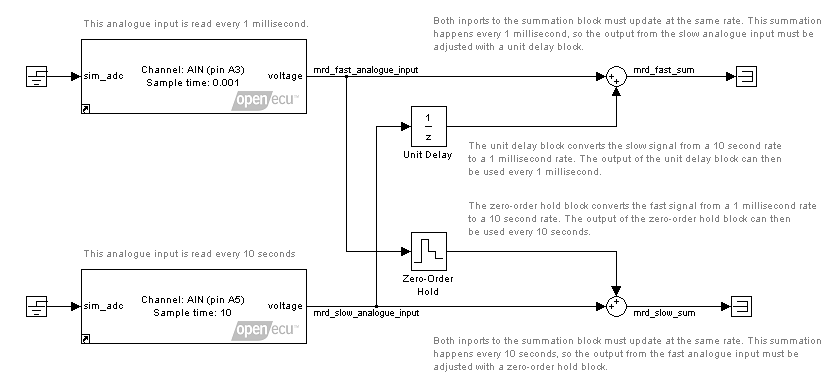
Multi-rate demo
This model shows how blocks can be put in different tasks by setting different sample rates. Additionally, values can be passed between tasks of different rates by using unit-delay and zero-order hold blocks.
Fixed angular demo
This model demonstrates use of the PAN feature.
Included is the method of setting us an angular task by creating a triggered subsystem from the TDC-firing trigger output by pan_EngineConfig.
The angular task is a simple tasks which reads inputs and sets the injector for the current cylinder.
IO demo
This model demonstrates the use of various IO blocks
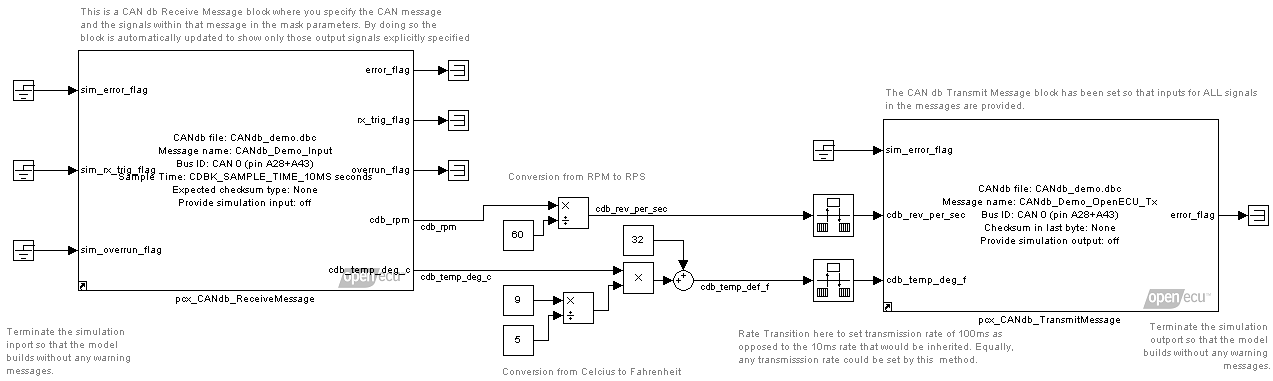
CANdb demo
This model demonstrates the basics of OpenECU's CANdb Support to transmit and receive messages in a model.
Extended Diagnostics
This model demonstrates the features described in the Extended Diagnostics page.
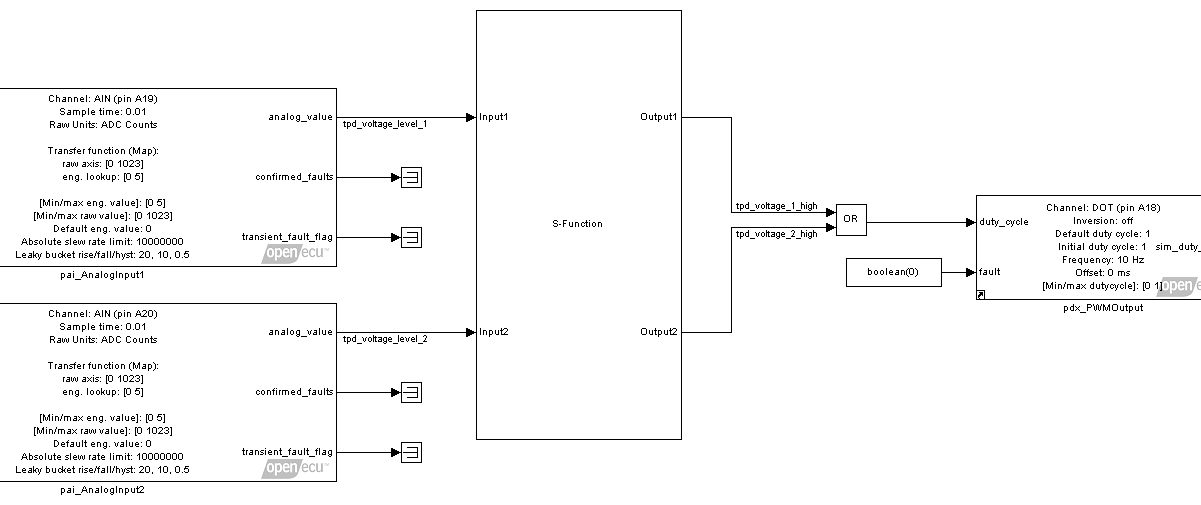
Two pot with S-Function
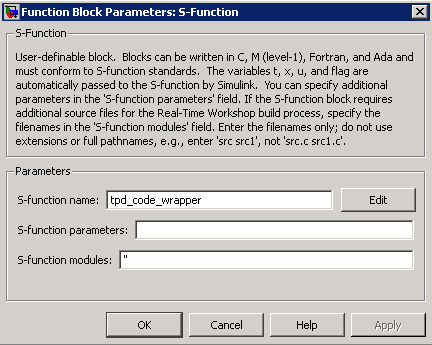
This model demonstrates using an s-function to create customer block behavior in the C programming language.
The s-function block points to a customer .c file which specifies the block's IO and behavior.
NVM demo
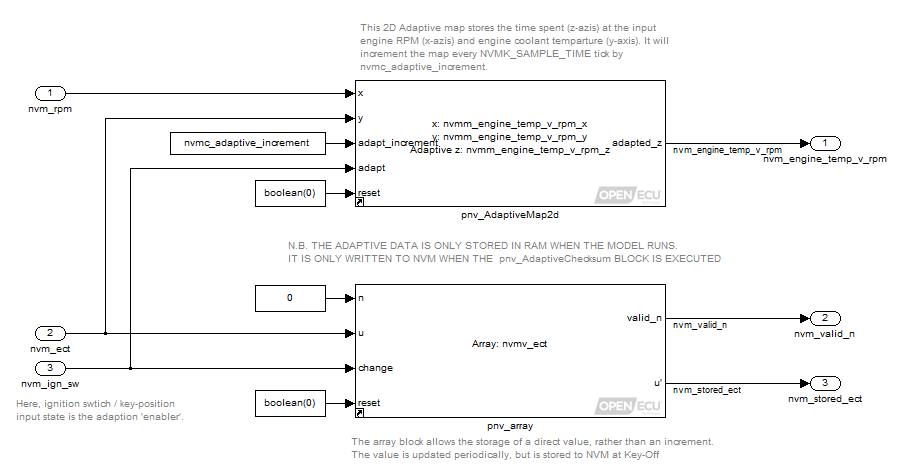
This model demonstrates the basic features of using the NVM blocks.
The model contains a pnv_AdaptiveMap2d block and a pnv_Array block, where the adaptive values are read and written. The user guide links explain what each of the inports and outports do.
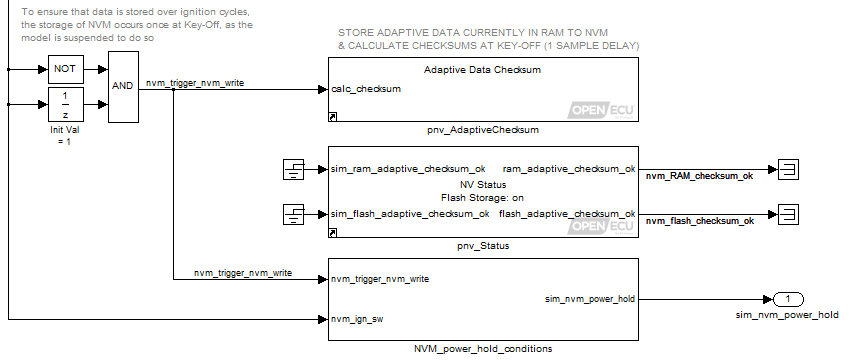
The model contains a pnv_AdaptiveChecksum block. Which is used to write the adapted values back to flash to persist their values. Also present is a pnv_Status block which provides status information on the state of adaptive memory data.
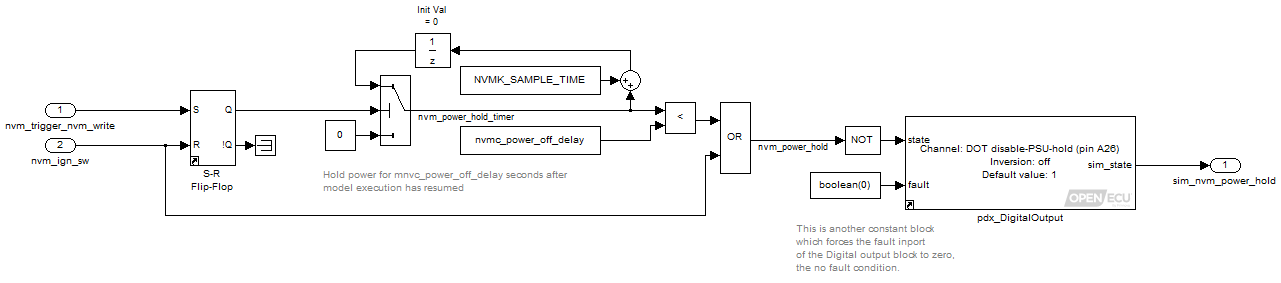
The model also contains a power-hold subsystem to keep the ECU on while NVM is written
A common practice is to update the NVM values at the end of the ECU's ignition cycle. When the ignition is turned off, this model keeps the ECU powered for a brief time while it updates the NVM values and then powers down the ECU when it is complete.
Learn more about power-hold on ECU Power Control.