Pulse the output channel pin at a fixed frequency and variable duty cycle.
None (Main library). (See Section 2.3, “Licensed Features”.)
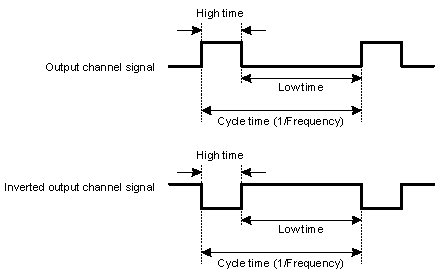
The PWM output block causes the channel output pin to oscillate at a desired frequency and duty cycle. The duty cycle is the High time divided by the Cycle time.
The actual state of the output pin is determined by the polarity of the pin. Some outputs are low-side only, some are high-side only, and some are software selectable. For software selectable pins, the polarity of the output can be selected by using the pdx_DigitalOutput block with the DOT select-high-side signal for the associated pin. Refer to the technical specification section for details on which pins support which polarities on each target.
Regardless of polarity, if the output is non-inverted, the output pin will be active during the High time and the output pin will be off (high impedance) during the Low time. If the output is inverted, the output will be active during the Low time and off during the High time.
This block calculates the output duty cycle as:
output duty cycle = Minimum duty cycle + (Maximum duty cycle - Minimum duty cycle) * duty_cycle
If the Minimum duty cycle is 0 and the inport duty_cycle is 0, the output channel state is set low and does not oscillate. When the Maximum duty cycle is 1 and the inport Duty_cycle is 1, the output channel state is set high and does not oscillate.
The block supports 0% and 100% duty cycles, where the output signal no longer pulses. A 0% duty cycle is defined as High time equals zero and 100% duty cycle is defined as Low time equals zero.
The channel output pin state can be inverted in order to achieve the desired logical output state.
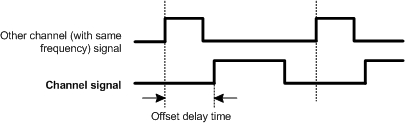
The channel output can be offset from other PWM channels of the same frequency. The {Offset} parameter is used to delay the start of the PWM cycle, so that the PWM pulse will not occur at the same time as other PWM signals of the same frequency.
If the inport fault input is nonzero, then the output is set to the default duty cycle mask parameter. The default duty cycle is never inverted and can only be set to zero or one so care should be taken to chose the appropriate value to disable the output during a fault condition.
The channel pin for this pwm output.
Value type: List Calibratable: No Inverts the mapping of the input value to the channel pin. If inversion is ticked then a logical NOT operation is applied to the output state.
Value type: Boolean Calibratable: No This value is used if fault is active. The value is mapped directly to the output channel and is never inverted. Care should be taken to choose the appropriate value to drive the output off.
Range: 0 or 1 duty-cycle
Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline and online The duty cycle that is output before the block has first been executed. This value is used in a similar way to Default duty cycle in that it is never inverted, however it can be set anywhere in the range 0 to 1.
Range: [0, 1] duty-cycle
Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline and online The frequency of the pwm signal.
Range: [0.5, 10000] Hz
Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline and online The desired phase offset, in milliseconds, of the PWM output, relative to other PWM output channels that have been configured with the same frequency.
Range: Target dependent
Target Range M110 Not supported M220 Not supported M221 Not supported M250 [0, 2000] ms M460 [0, 2000] ms M461 Not supported M670 Not supported Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline Must be in the range 0 to (Maximum duty cycle - 0.1).
Range: [0, 0.9] duty-cycle
Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline and online Must be in the range (Minimum duty cycle + 0.1) to 1.0.
Range: [0.1, 1] duty-cycle
Value type: Real Calibratable: Yes, offline and online Tick to enable outport sim_duty_cycle.
Value type: Boolean Calibratable: No
The resolution of the PWM channels depends on the output device (specified in the hardware target tables in Section 1.1, “ECU hardware reference documentation”). Some channels have better resolution that others.
Some of the PWM output channels do not produce an accurate wave form when the duty cycle is either very small (e.g., 0.5%) or very large (e.g., 99.5%). All PWM output channels cope with 0% and 100% duty cycles correctly.
For the M250 target specifically, in order to avoid shoot-through and damage to the ECU when the mode switches, a 100us dead-time is inserted in the PWM signal for one task cycle at the beginning of mode-transition. Additionally, this dead-time insertion will only occur if the duty cycle that is commanded has a low time of less than 100us. For this reason, it will not be possible to command a 100% duty cycle during mode-transition for one task period.