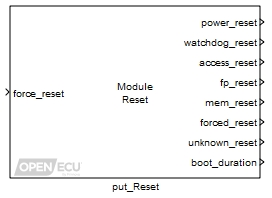
Provide reset information and a mechanism to reset the ECU.
None (Main library). (See Section 2.3, “Licensed Features”.)
Allow the user to force the module to reset. Provide information about the previous reset event including how long the module took to start iterating the model.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was from a power up event, 0 otherwise.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was due to the ECU's processor watchdog, 0 otherwise.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was due to incorrect software in the model or platform accessing a memory area in the controller that did not exist, 0 otherwise.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was due to incorrect software in the model that attempted to manipulate a floating point value in a way the ECU's processor determined as invalid, 0 otherwise. Note that floating point exceptions are not enabled on all platforms and as such the lack of a floating point reset is not sufficient to prove that the model is free from floating point manipulation errors.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was due to an unrecoverable corruption of internal memory, 0 otherwise. The cause of a reset that occurs as a result of memory corruption may not always be identified by software. If the cause cannot be identified by the platform software, then the reset will be reported by the unknown_reset outport.
Set to 1 if the last reset event was due to a forced model reset, 0 otherwise.
Set to 1 if the last reset event could not be determined, 0 otherwise.
A rough indication of how long the module took to boot (i.e., from processor start to starting the first model iteration) in seconds. Only if the version of boot is sufficient (version 1.0.7 or greater) will this outport contain a value. If the boot version is not sufficient, the outport is set to zero.
Note
The duration from power up to processor start is not part of boot_duration. It varies based on the environmental conditions but is usually around 40ms to 80ms in duration. The boot duration will increase as the calibration size increases.